This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Scientists have made a major breakthrough that could help us understand the origin of our universe, they say.
Researchers have discovered hints of a difference between the behaviour of neutronos and antineutrinos. That, in turn, could help demonstrate why there is so much matter relative to antimatter in the universe – and, in turn, how everything that surrounds us came to be.
One of the greatest challenges in understanding the universe arises from the fact that the Big Bang should have created the universe with equal amounts of antimatter and matter. Observations of the cosmos, however, show that it is made of matter – and researchers have struggled to explain where that missing antimatter may have gone.
To explain the universe's existence, scientists think there must be something different about matter and antimatter, which would explain why the universe appears to favour one over the other. The new breakthrough may reveal where that asymmetry has come from.
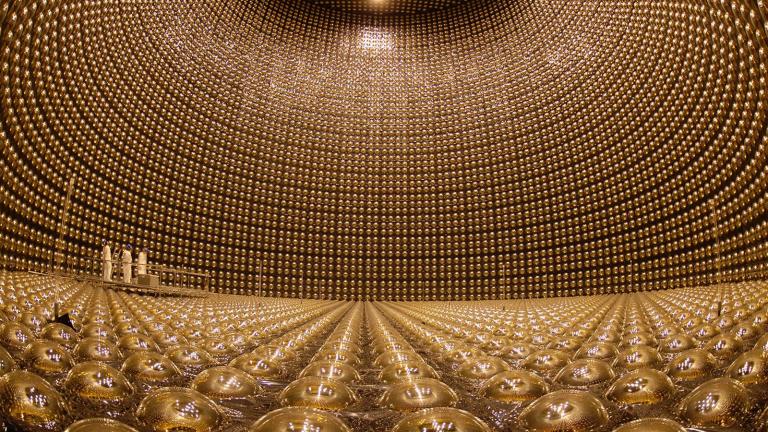
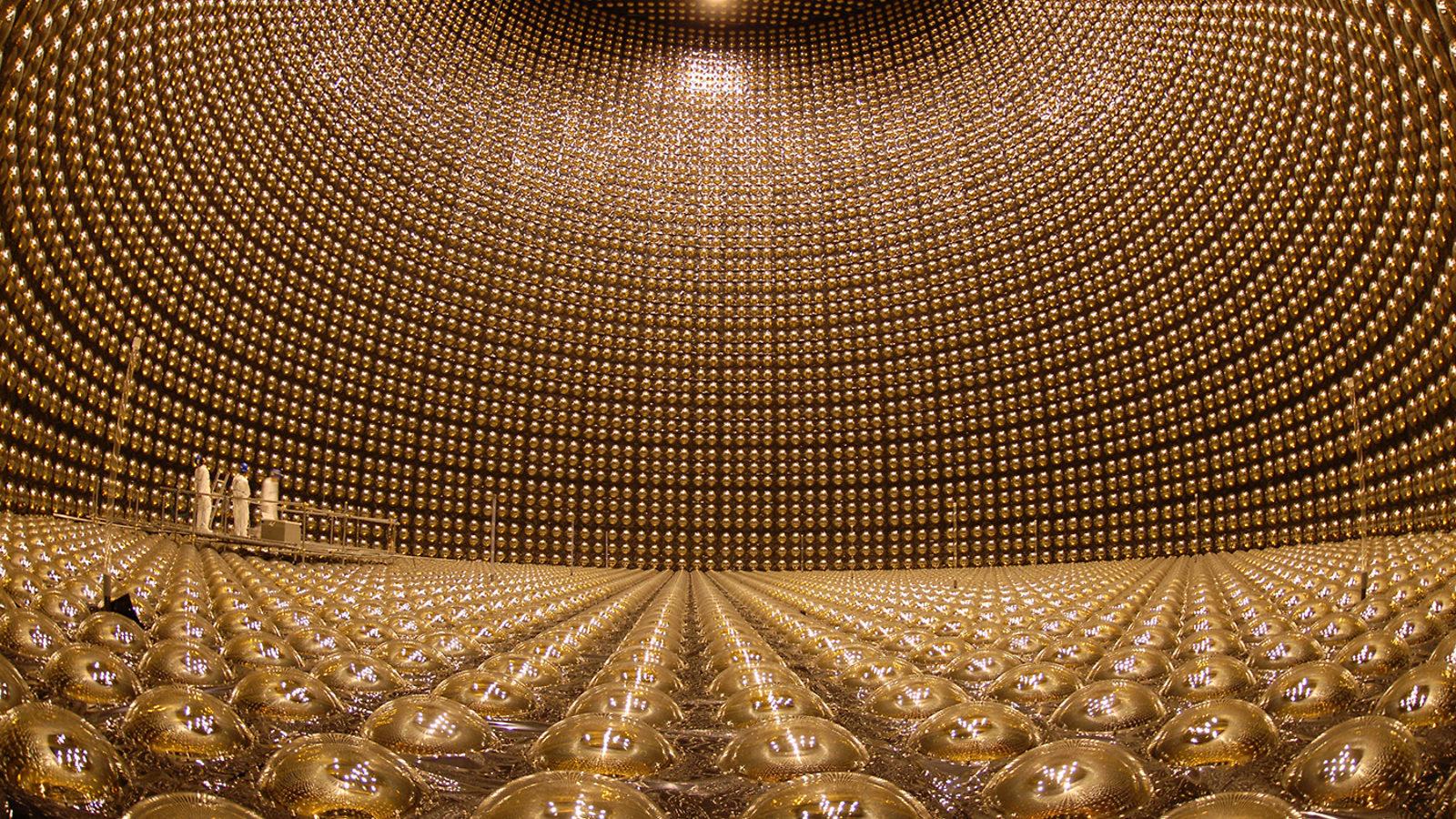
The new discoveries come from the T2K experiment in Japan. There, researchers at one detector watch neutrinos and antineutrinos that are generated almost 300 kilometres away at the Japanese Proton Accelerator Research Complex.
As they travel between the two, and through the Earth, the particles switch between different properties known as flavours. The new research showed that the neutrinos and antineutronos do that, by observing what flavour the different particles had when they were created.
After nine years of such observations, the experiment found that there is something different between the fundamental particles, which could help explain the difference that is seen through the universe, though they caution that further research is needed to confirm the discoveries.
"Our data continue to suggest that Nature prefers almost the maximal value of asymmetry for this process," said Laura Kormos, senior lecturer in physics at Lancaster University, head of Lancaster's neutrino physics group and researcher at T2K. "It would be just like Mother Nature to have these seemingly insignificant, difficult to study, tiny particles be the driver for the existence of the universe."
Created with Sketch.
Created with Sketch.
1/10
Mystic Mountain, a pillar of gas and dust standing at three-light-years tall, bursting with jets of gas flom fledgling stars buried within, was captured by Nasa's Hubble Space Telelscope in February 2010
Nasa/ESA/STScI
2/10
The first ever selfie taken on an alien planet, captured by Nasa's Curiosity Rover in the early days of its mission to explore Mars in 2012
Nasa/JPL-Caltech/MSSS
3/10
Death of a star: This image from Nasa's Chandra X-ray telescope shows the supernova of Tycho, a star in our Milky Way galaxy
Nasa
4/10
Arrokoth, the most distant object ever explored, pictured here on 1 January 2019 by a camera on Nasa's New Horizons spaceraft at a distance of 4.1 billion miles from Earth
Getty
5/10
An image of the Large Magellanic Cloud galaxy seen in infrared light by the Herschel Space Observatory in January 2012. Regions of space such as this are where new stars are born from a mixture of elements and cosmic dust
Nasa
6/10
The first ever image of a black hole, captured by the Event Horizon telescope, as part of a global collaboration involving Nasa, and released on 10 April 2019. The image reveals the black hole at the centre of Messier 87, a massive galaxy in the nearby Virgo galaxy cluster. This black hole resides about 54 million light-years from Earth
Getty
7/10
Pluto, as pictured by Nasa's New Horizons spacecraft as it flew over the dwarf planet for the first time ever in July 2015
Nasa/APL/SwRI
8/10
A coronal mass ejection as seen by the Chandra Observatory in 2019. This is the first time that Chandra has detected this phenomenon from a star other than the Sun
Nasa
9/10
Dark, narrow, 100 meter-long streaks running downhill on the surface Mars were believed to be evidence of contemporary flowing water. It has since been suggested that they may instead be formed by flowing sand
Nasa/JPL/University of Arizona
10/10
Morning Aurora: Nasa astronaut Scott Kelly captured this photograph of the green lights of the aurora from the International Space Station in October 2015
Nasa/Scott Kelly
1/10
Mystic Mountain, a pillar of gas and dust standing at three-light-years tall, bursting with jets of gas flom fledgling stars buried within, was captured by Nasa's Hubble Space Telelscope in February 2010
Nasa/ESA/STScI
2/10
The first ever selfie taken on an alien planet, captured by Nasa's Curiosity Rover in the early days of its mission to explore Mars in 2012
Nasa/JPL-Caltech/MSSS
3/10
Death of a star: This image from Nasa's Chandra X-ray telescope shows the supernova of Tycho, a star in our Milky Way galaxy
Nasa
4/10
Arrokoth, the most distant object ever explored, pictured here on 1 January 2019 by a camera on Nasa's New Horizons spaceraft at a distance of 4.1 billion miles from Earth
Getty
5/10
An image of the Large Magellanic Cloud galaxy seen in infrared light by the Herschel Space Observatory in January 2012. Regions of space such as this are where new stars are born from a mixture of elements and cosmic dust
Nasa
6/10
The first ever image of a black hole, captured by the Event Horizon telescope, as part of a global collaboration involving Nasa, and released on 10 April 2019. The image reveals the black hole at the centre of Messier 87, a massive galaxy in the nearby Virgo galaxy cluster. This black hole resides about 54 million light-years from Earth
Getty
7/10
Pluto, as pictured by Nasa's New Horizons spacecraft as it flew over the dwarf planet for the first time ever in July 2015
Nasa/APL/SwRI
8/10
A coronal mass ejection as seen by the Chandra Observatory in 2019. This is the first time that Chandra has detected this phenomenon from a star other than the Sun
Nasa
9/10
Dark, narrow, 100 meter-long streaks running downhill on the surface Mars were believed to be evidence of contemporary flowing water. It has since been suggested that they may instead be formed by flowing sand
Nasa/JPL/University of Arizona
10/10
Morning Aurora: Nasa astronaut Scott Kelly captured this photograph of the green lights of the aurora from the International Space Station in October 2015
Nasa/Scott Kelly
If it is confirmed, and further planned experiments go ahead, then the discovery could help find the so-called missing antimatter that has perplexed scientists as they hunt for an explanation of the strange mismatch throughout the universe, and the origin of the cosmos.
The new study, 'Constraint on the matter–antimatter symmetry-violating phase in neutrino oscillations', is published in the latest edition of Nature.



 Africana55 Radio
Africana55 Radio 

